
Graphic design is the art of visual communication. This 2025 guide for beginners will walk you through the fundamentals, principles, and various types of graphic design, tailored for beginners. We’ve included examples, resources, expert insights, and visuals to help you grasp the concepts easily.
If you’ve ever been captivated by a striking poster, an ad, a website, or even the packaging of your favorite products, you’ve experienced the power of graphic design. It’s everywhere! But what exactly is graphic design?
What is Graphic Design in Simple Terms?
Graphic design is the practice of creating visual content using typography, images, colors, and shapes to convey a message. The ultimate goal is to make information easy to understand and visually appealing.
As humans, we’re naturally drawn to visuals, and graphic design capitalizes on this. Over the years, graphic design has evolved from calligraphy and printing presses during the Industrial Revolution to a dynamic digital field in the 21st century.
Can You Learn Graphic Design on Your Own?
Yes, you absolutely can! With dedication and consistent practice, you can master graphic design. There are countless resources like courses, tutorials, books, and podcasts to guide your journey.
Here’s what Alina Wheeler, a self-taught graphic designer, has to say:
“Design is intelligence made visible. Anyone can learn to see and create beauty with time, observation, and practice. The key is patience and a willingness to explore.” – Alina Wheeler, Author of Designing Brand Identity
The Fundamentals of Graphic Design
Graphic design isn’t just about creativity; it’s about mastering key principles and elements that make a design work. Let’s explore these essentials:
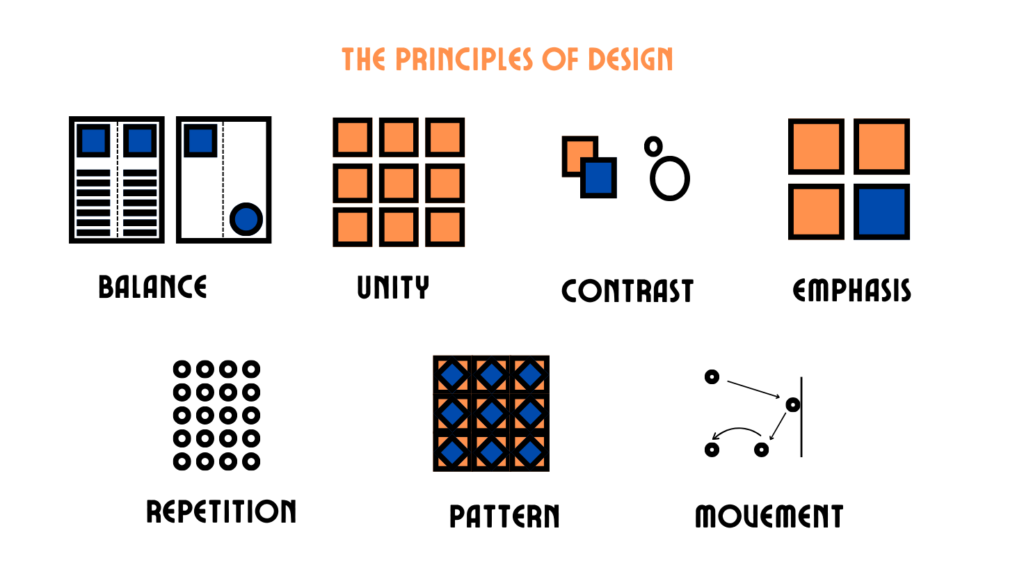
Principles of Design
- Contrast: Highlights differences between elements like color, size, or type to draw attention and create hierarchy.
- Repetition: Reinforces a consistent visual message by reusing design elements.
- Alignment: Arranges elements neatly to guide the viewer’s eye and create clean designs.
- Proximity: Groups related elements together for better organization and coherence.
- Balance: Distributes visual weight evenly across a design, whether symmetrical or asymmetrical.
- Space: Uses negative space to define importance, separate elements, or create clarity.
Pro Tip: Use the acronym CRAP (Contrast, Repetition, Alignment, Proximity) to remember these principles!
Principles of DesignGraphic Design Elements
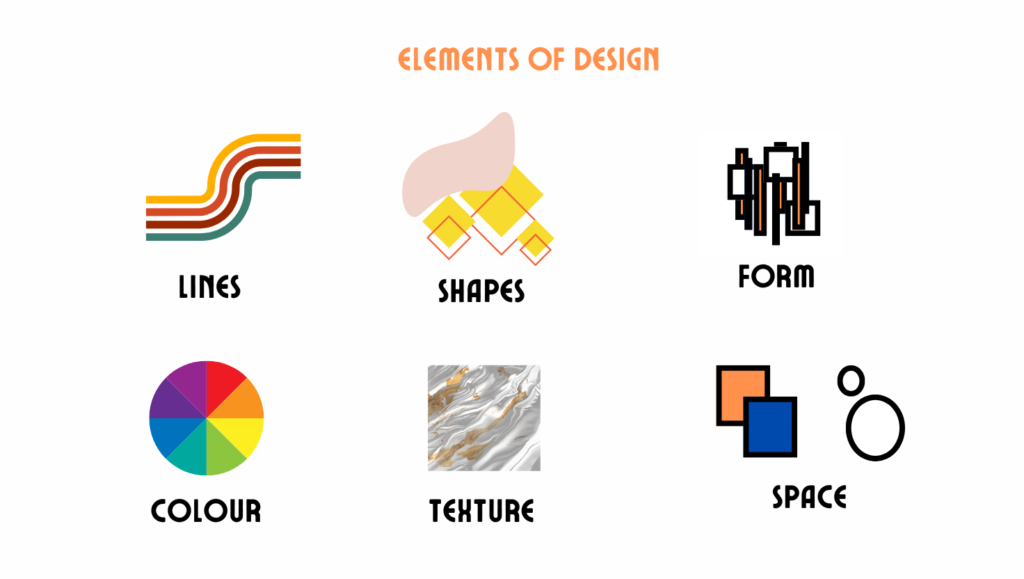
- Line: Defines space, guides the viewer’s eye, and creates structure.
- Shape: Adds interest and depth, whether geometric or organic.
- Color: Evokes emotion, sets the mood, and conveys symbolic meaning.
- Texture: Enhances depth and sensory appeal.
- Typography: Plays with fonts and text arrangement to improve readability and style.
These principles and elements come together to create visually harmonious designs that effectively communicate messages.
Types of Graphic Design
Graphic design spans many fields, offering a range of career opportunities. Let’s explore the most common types of graphic design and their real-world applications:
1. Brand Identity Graphic Design
This involves creating logos, typography, colour schemes, and visual elements that define a brand’s personality. Designers in this field must also understand branding concepts like tone of voice and personality.

“Design is the silent ambassador of your brand.” – Paul Rand
2. Marketing and Advertising Graphic Design
Designers in this area focus on promotional materials like social media ads, brochures, and posters. Their goal is to attract and engage audiences while adhering to brand guidelines.

3. Web and UI Design
Also known as User Interface (UI) design, this field involves creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces for websites and apps.
4. Print and Publication Design
This involves crafting layouts for physical materials like magazines, newspapers, and books. Print designers focus on making content both engaging and easy to read.
5. Packaging Design
Packaging design combines aesthetics and functionality to make products stand out. This includes logos, product details, and branding elements.

6. Motion Graphics Design
Motion design combines video, animation, and sound to create dynamic visuals, commonly used in digital ads, films, and games.
Examples of tasks:
- Creating animated logos
- Designing video overlays and effects
- Composing interactive visuals
7. Illustration Design
Illustration focuses on bespoke artwork for books, packaging, merchandise, and branding. This is the more artistic side of graphic design.
Examples of tasks:
- Designing book covers or product labels
- Creating custom artwork for campaigns
- Adding personalized elements to brand visuals
8. Environmental Design
This combines graphic design with architecture and interior design to create immersive experiences in physical spaces.
Examples of tasks:
- Designing murals and signage
- Branding office interiors
- Creating museum exhibits
The Graphic Design Process
The design process varies between projects, but it generally follows these five steps:
- Briefing: Understand the client’s needs, goals, and target audience.
- Research: Analyze the market, competitors, and industry trends.
- Conceptualization: Brainstorm ideas and create mood boards.
- Design Development: Build prototypes and refine designs.
- Final Production: Deliver polished files in the required formats.
Designers often conduct feedback sessions post-project to improve collaboration and results for future work.
Essential Tools for Graphic Designers
To succeed in graphic design, you’ll need a mix of creativity and the right tools:
- Design Software: Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign), Figma, Sketch
- Collaboration Tools: Slack, Trello, Asana
- Typography Resources: Google Fonts, Adobe Fonts
- Stock Resources: Unsplash, Pexels, Flaticon
- Feedback Tools: Miro, InVision, Zeplin
AI and Graphic Design in 2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming graphic design, automating tasks like layout generation, color selection, and market analysis. However, creativity and human intuition remain irreplaceable. Designers who embrace AI as a collaborative tool can achieve greater efficiency and innovation.
Careers in Graphic Design
A career in graphic design doesn’t necessarily require a formal degree. A strong portfolio showcasing your creativity and technical skills can be just as valuable. Practical experience through internships or freelance work is highly recommended.
Beginner-Friendly Resources:
- Courses: Skillshare , Coursera , LinkedIn Learning
- Books: Graphic Design School by David Dabner, Thinking with Type by Ellen Lupton
- YouTube Channels: The Futur, Envato Tuts, Satori Graphics
PariPixel Studio – Turning ideas into visuals that captivate!



